Code Scanning
The Code Scanning module in DeepTraQ allows you to detect security vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance issues directly in your code repositories. It supports multiple source code hosting platforms, identifies vulnerable libraries, insecure coding practices, and provides actionable recommendations to remediate risks before deployment.
Supported platforms:
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Bitbucket
Supported programming languages and ecosystems:
- Python, Node.js, Maven, Go, Composer, Erlang, GitHub Actions, NuGet, Pub, RubyGems, Rust, Swift
How It Works
- Repository Access – Connect to your repository via a Personal Access Token (PAT) for authenticated scans. Public repositories can be scanned without authentication.
- Code Analysis – DeepTraQ scans the code base, including dependency manifests and build configuration files, for security issues and misconfigurations.
- Vulnerability Mapping – Detected issues are cross-referenced with:
- NVD CVEs
- CWE mappings
- Language-specific advisory databases (PyPI, npm, Maven Central, RubyGems, etc.)
- Library Inventory – All dependencies and their versions are listed, highlighting vulnerable or outdated packages.
- Reporting & Insights – Results are displayed in a centralized dashboard with summary metrics, vulnerabilities details, library information, and scan history.
Requirements
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Repository Access | Read access to GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket repositories |
| Authentication | Personal Access Token (PAT) for private repositories |
| Supported Languages | Python, Node.js, Maven, Go, Composer, Erlang, GitHub Actions, NuGet, Pub, RubyGems, Rust, Swift |
| Repository URL | Full repository URL for scanning (HTTPS or SSH) |
| Optional | Custom branch/tag selection for scanning specific versions |
Ensure that the token provided has read-only access to the repository to maintain security.
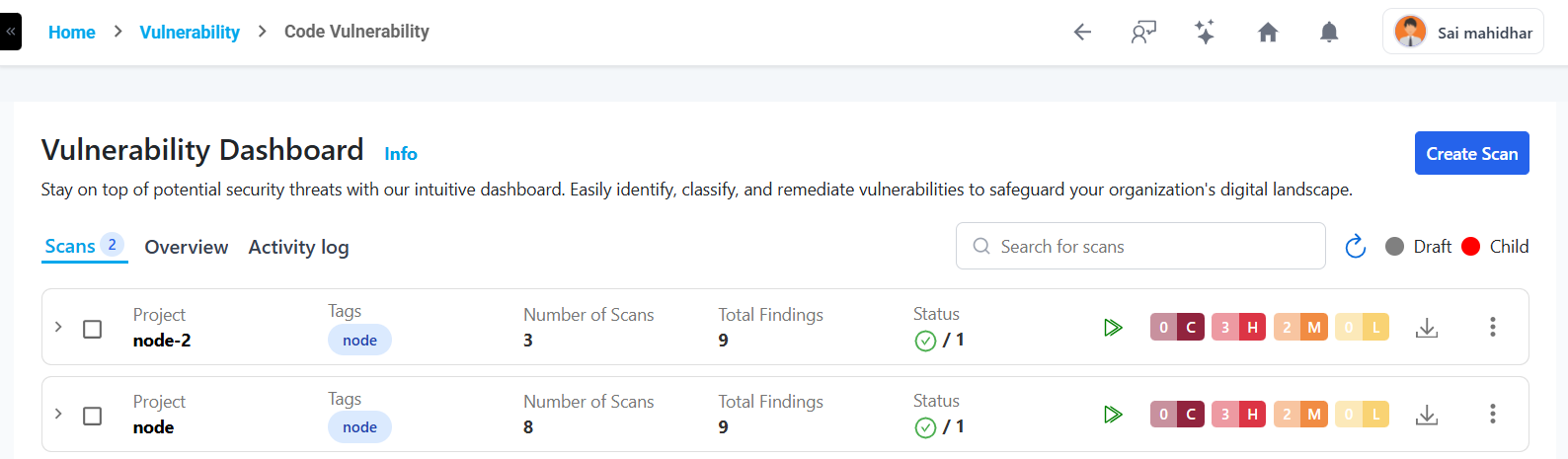
Creating New Scan
- Navigate to Code Scanning from the dashboard.
- Click Create New Scan.
- Enter the following details:
- Scan Name – A unique identifier for the scan
- Repository URL – HTTPS or SSH URL of the repository
- Branch/Tag – Optional, default is
main - Authentication Method –
PAT Tokenor public repo - Optional Labels / Tags – e.g.,
frontend,backend,microservice
- Select the programming languages or ecosystems to include in the scan.
- Click Start Scan.
View placeholder image for Creating Code Scan
Managing Existing Scans
After creating a scan, navigate to the Code Scans list to view all configured scans in an accordion-style layout.
Each scan entry displays:
- Project (Scan Name)
- Repository URL
- Branch / Tag
- Scan Status (Done, Running, Failed, Partially Done)
- Last Scan Findings (Total vulnerabilities found)
- Severity Summary (Critical, High, Medium, Low)
Run Icon – Execute a scan manually Three-dot menu (⋮) – Edit, duplicate, export, or delete
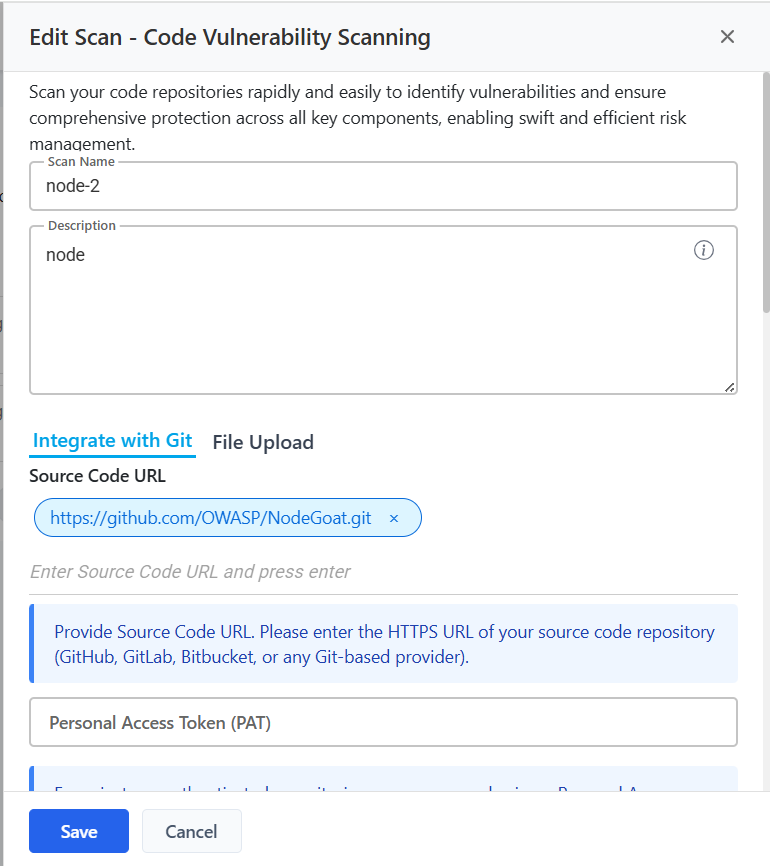
Editing Scans
- Modify Scan Name / Repository URL / Branch / Tags
- Update Authentication Method or PAT Token
- Change Scheduling Options
Note: Repository platform (GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket) cannot be changed after scan creation.
View placeholder image for Editing Code Scan
Viewing Scan Results
Code scanning results are displayed across the following tabs:
Summary Tab
- High-level overview of the scan results:
- Total vulnerabilities
- Severity breakdown (Critical, High, Medium, Low)
- Library health (outdated or vulnerable packages)
- Repository and branch info
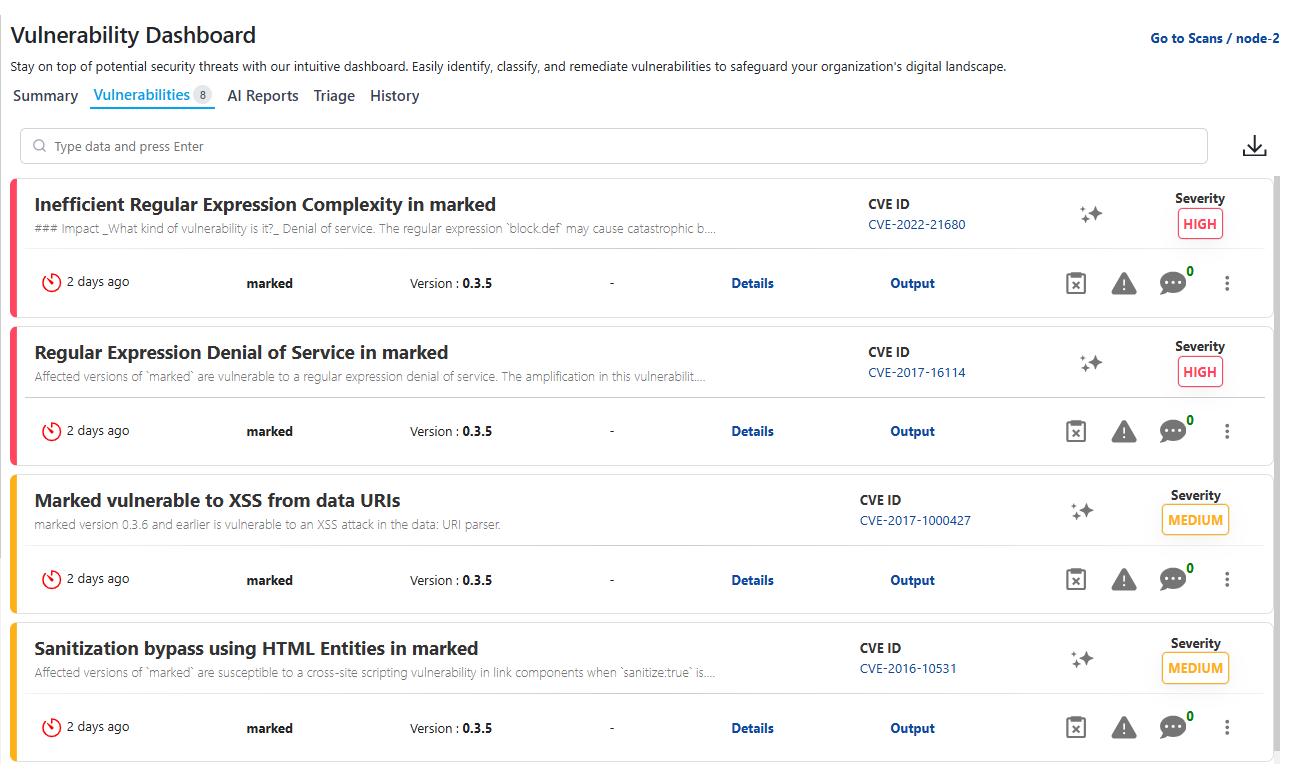
Vulnerabilities Tab
Displays detailed information about each detected vulnerability:
- CVE / Advisory ID
- Package / Library Name
- Version
- Severity (Critical / High / Medium / Low)
- CWE Mapping
- Description & Risk
- Remediation
- References (NVD, Language Advisory, Vendor Docs)
View placeholder image for Vulnerabilities Tab
History Tab
- Displays all previous scans, including:
- Timestamp
- Duration
- Scan Status
- Total vulnerabilities
- Comparison with previous scans (New / Resolved)
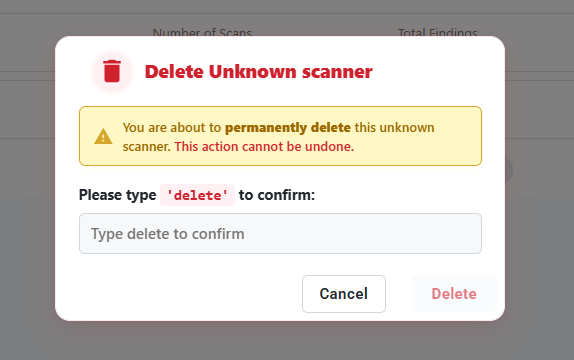
Deleting Scan
- Click the three-dot menu (⋮) → Delete
- To delete multiple scans, select checkboxes and click Delete
- Confirm deletion by typing
DELETE
View placeholder image for Deleting Scan
Scanning Limits
- Maximum repositories per scan: 1 repository per scan
- Maximum branches per scan: 1 branch
- Concurrent scans per organization: Up to 10
For large monorepos, consider splitting into multiple scans by service or directory.
Launching Scan
- Manual Execution: Click the Run Icon on a scan in the accordion.
- Scheduled Scans: Configure periodic scans (Daily, Weekly, Monthly).
- Branch / Tag Selection: Only selected branch/tag will be scanned.
View placeholder image for Launching Scan
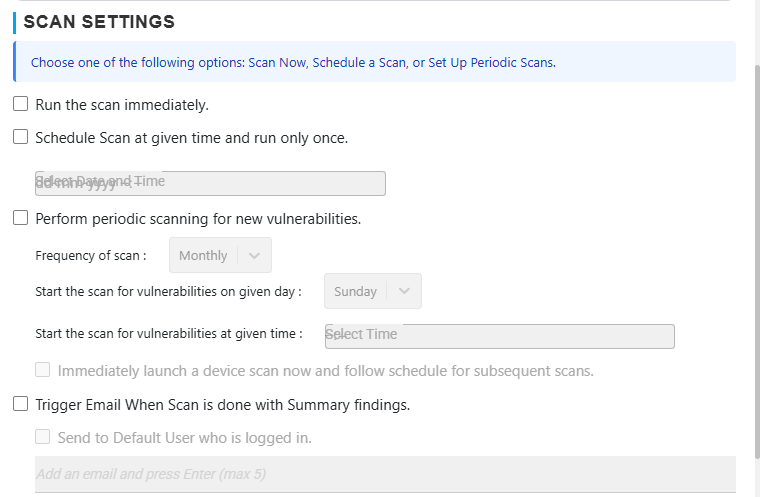
Email Notifications
Notifications are sent when:
- Scan completes (summary and vulnerabilities)
- Scheduled scan starts
- Optional: Only for high severity vulnerabilities
Troubleshooting Scan Errors
- Failed Scan – Could be due to invalid credentials, repo not found, or network issues
- Error Logs – Click History → ⋮ → Errors to view stack trace and error messages
Example:
Error: Invalid Personal Access Token
at Object.openSync (node:fs:596:3)
at perform_code_scan (/home/ubuntu/code-scanners/worker.js:114:21)
at async Worker.processJob